S3
S3 buckets are a reliable and scalable solution for storing artifacts. S3’s high availability makes it a great choice for handling large files and frequent update
Setting up an S3 Bucket
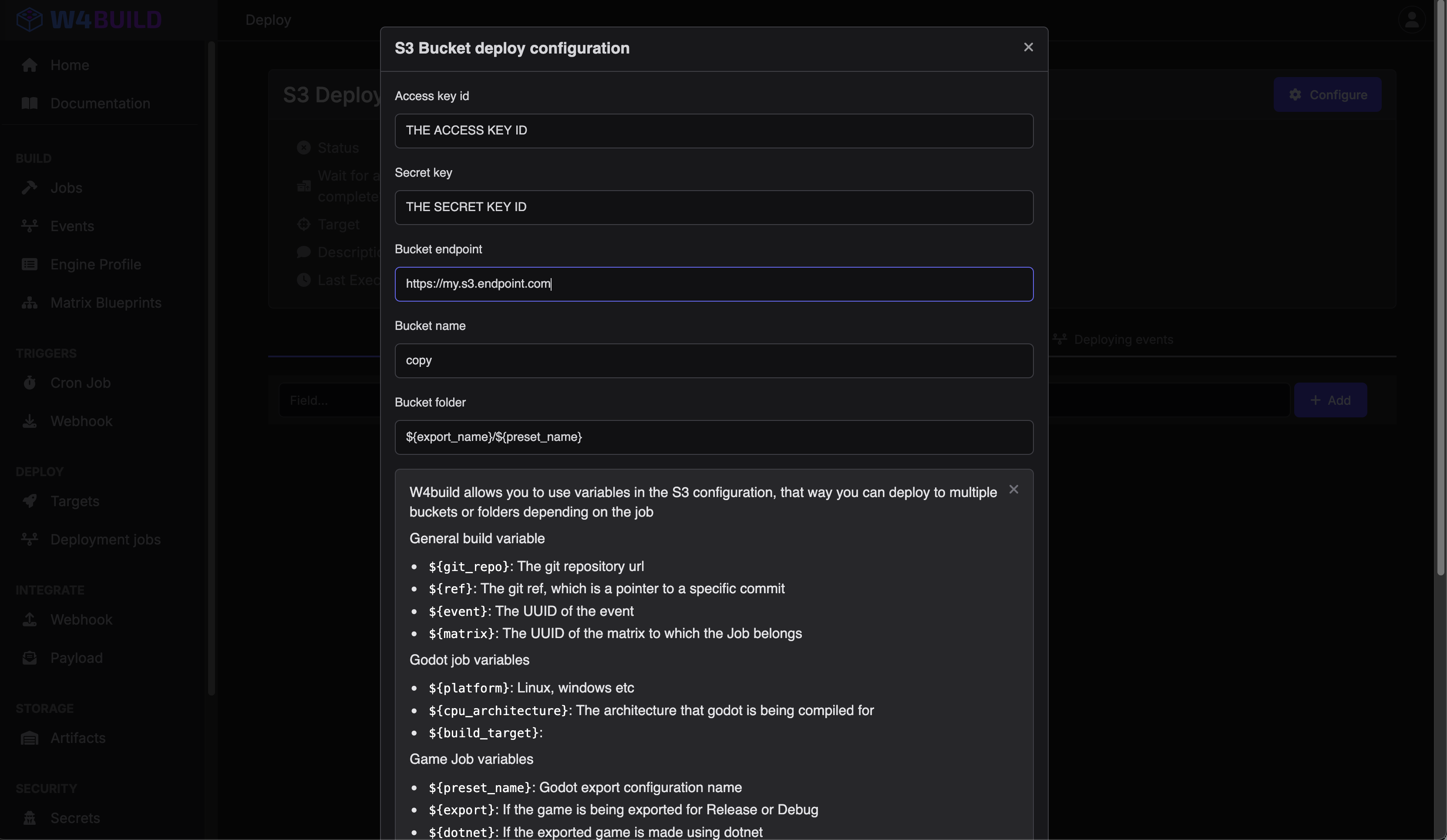
Creating an S3 bucket varies from provider to provider, so this guide will show what data you need.
Access Key ID
(behaves like the username) A unique identifier used to authenticate API requests made to the provider’s services. It is paired with a Secret Access Key to securely authorize actions on your account
Secret Access Key
(behaves like the password) A secret key used in conjunction with the Access Key ID to sign and authenticate requests to the provider’s services.
Bucket Endpoint
The URL that provides access to the storage bucket. The endpoint is typically region-specific, like provider.com or provider-region.com
Bucket Name
The unique name assigned to your storage bucket. It serves as the global identifier for your storage container and is used to reference the bucket in API calls
Bucket Folder
A logical grouping within an S3 bucket, they help organize objects within the bucket for easier management and access.
Setting up W4Build
Open w4build Targets page
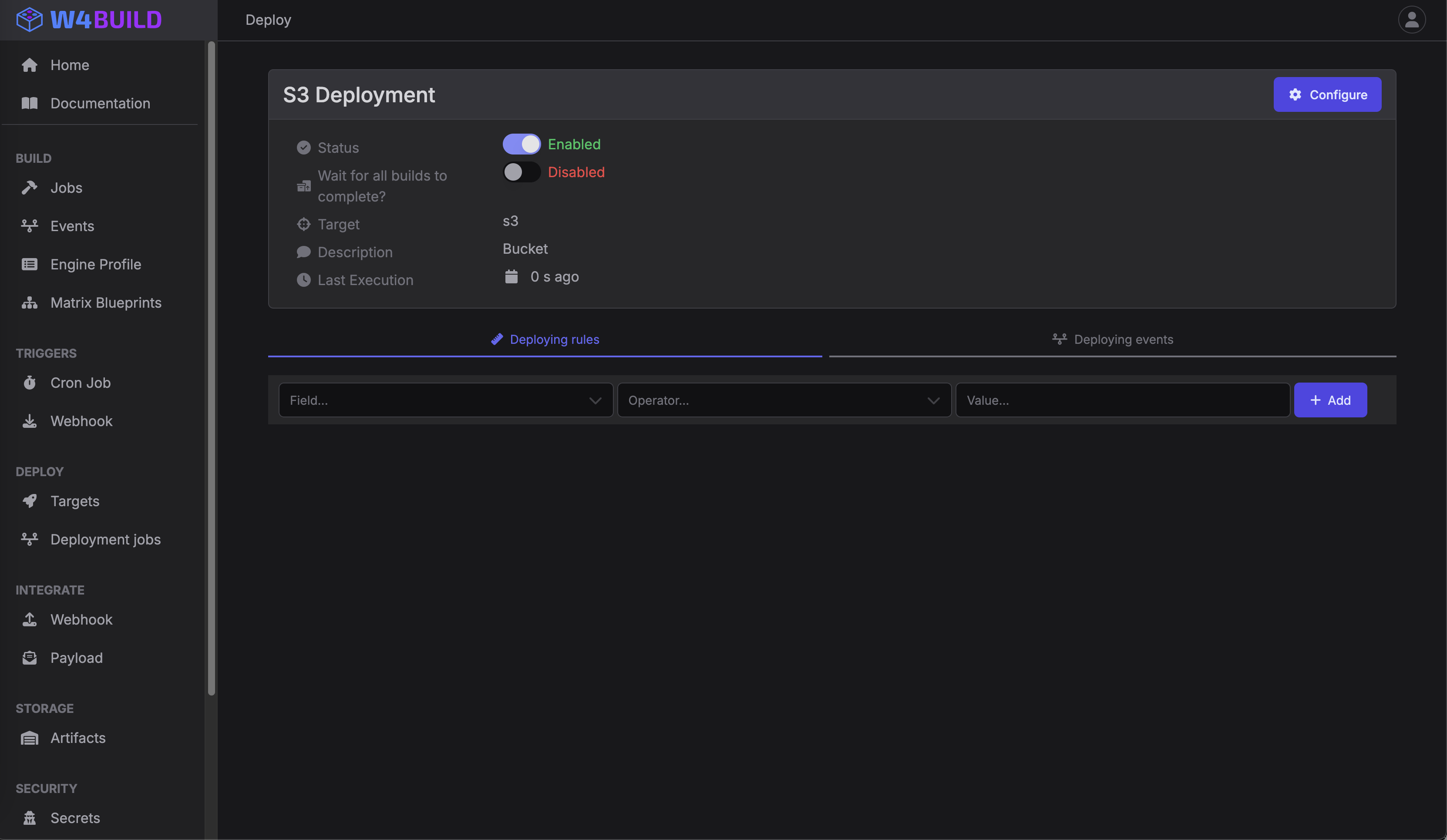
Click add target, and select S3
Click configure
Fill the form with all the values we described on the first section
Click save
Rules
Since this deployment will hold a backup of all files created, we want that all builds match and trigger the deployment. For thsi we add no rules
Important
After each build completes, the deployment process checks if it meets the required rules. If all rules are satisfied, the deployment is initiated. You can also configure deployments to wait for specific events, ensuring that the deployment only begins once all related builds in an event are finished.